Why Replace Metal with Plastics?
Carlos Martin
European Product Manager - DOMO Chemicals
Ultrapolymers Group
Carlos Martin is the European Product Manager for DOMO at Ultrapolymers, where he focuses on positioning DOMO's products within the portfolio. With over 14 years of experience in the polymer industry, specialising in engineering thermoplastics for automotive, E&E, medical, and consumer goods markets, Carlos' focus is in understanding customer needs and fostering long-lasting relationships based on trust and respect.
Why think about metal replacement?
The shift from metal to plastic is more than a trend - it's a strategic move that delivers tangible benefits. Appreciating the advantages of metal replacement will help you stay ahead of the competition. Key benefits of metal replacement include:
- Design Flexibility: Freedom in design enhances aesthetics and ergonomics, making your product stand out in the market.
- Cost & Supply Chain Optimisation: Polymers often reduce total production costs through faster processing, part integration, and fewer secondary operations.
- Advanced Property Profiles: Advanced polymers resist corrosion, offer excellent fatigue performance, and ensure long-term durability in demanding applications.
- Environmental Benefits: Lower CO₂ footprint solutions, recycled & recyclable polymers, and less energy-intensive manufacturing, help to achieve sustainability goals.
Design Flexibility
Switching from metal to plastic opens up a world of design possibilities. Versatile polymer processing, combined with modern advanced polymers, gives greater design freedom. This enables part consolidation, functionality integration, and the creation of aesthetic geometries that would otherwise be difficult and costly to scale with metals.
With plastics, integrating multiple functions into a single component eliminates costly assembly and post-moulding processes. Designing in ribs, bosses, and undercuts helps achieve the mechanical properties of metal. This also helps to optimise products for lightweighting, a recurring topic in the automotive sector. Modern injection moulding techniques enhance design flexibility by enabling intricate details and advanced tooling design that drives product originality.
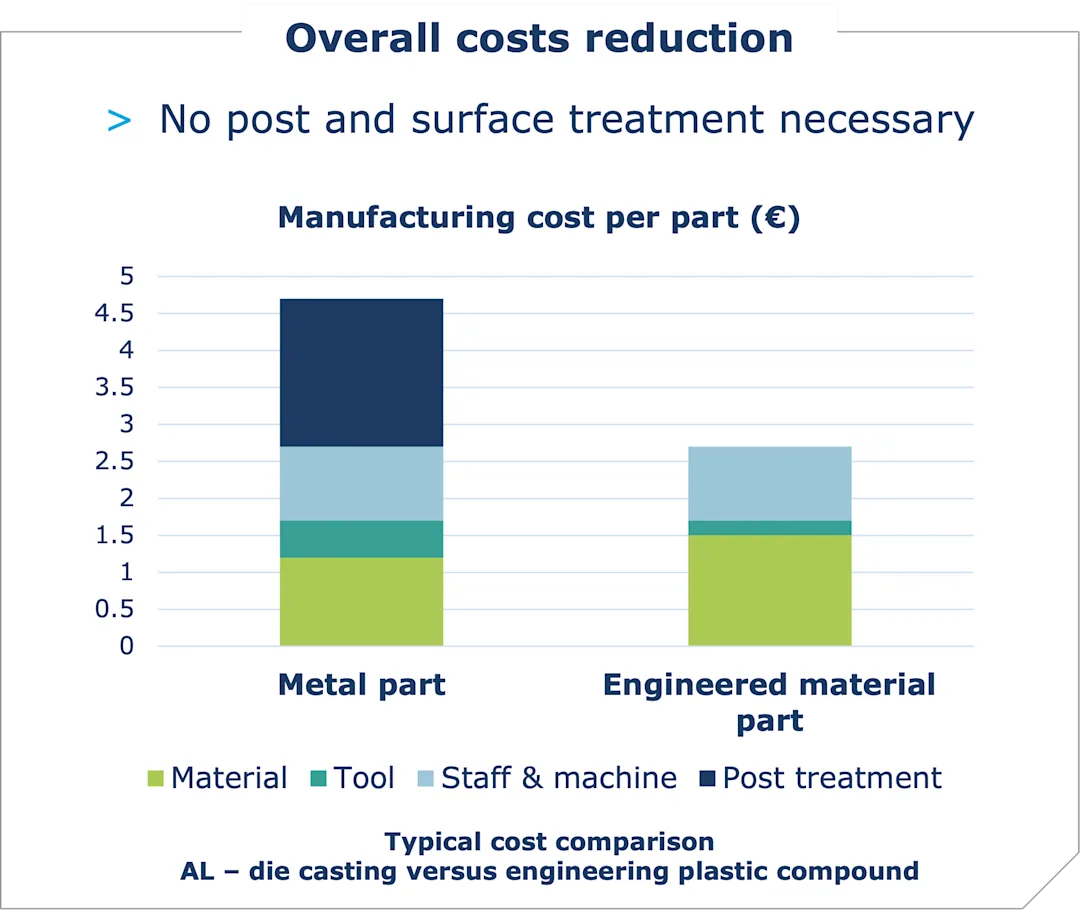
Cost & Supply Chain Optimisation
Although metal raw material is often cheaper than plastic, the overall price per part is significantly reduced with modern engineering thermoplastics:
- Tooling for polymers is more cost-effective than for metals. Tools for metal processing cost more to produce, and for some processes, must be replaced multiple times to achieve the same output as a polymer processing tool.
- Manufacturing automation with modern injection moulding machines and auxiliary robotics requires little to no staff interaction. Machinery for plastic processing is agile, and new machines are highly energy efficient.
- Post processes such as machining, surface treatments and painting are costly. Designing with function in mind enables plastic parts to be manufactured with no drilling or machining of features required. Polymer compounds come equipped with the additives and pigments to achieve the desired surface finish, including metallic finishes.
- Local sourcing of plastics reduces lead times and strengthens supply chains. By building in a local backup supply, organisations can better manage risk and respond to market changes.
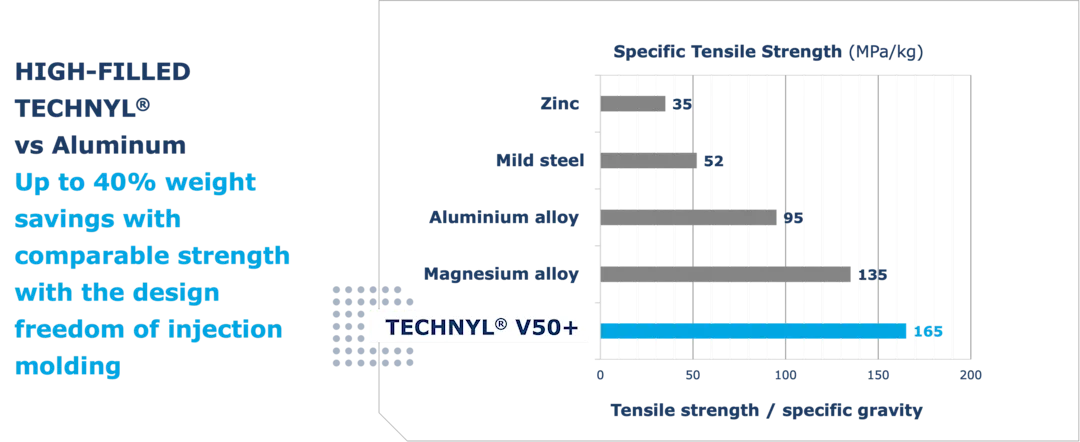
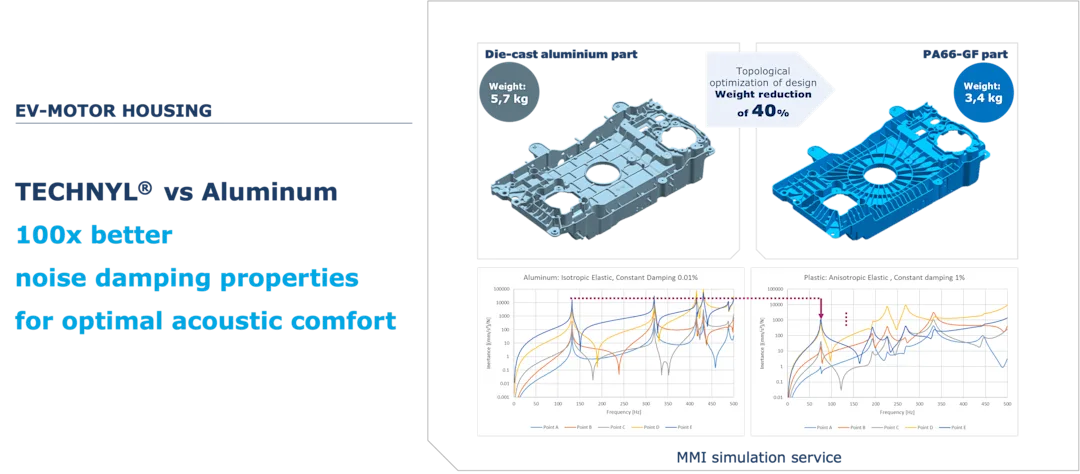
Advanced Property Profiles
Today's engineering polymers are designed to meet or even exceed the performance of metals in many demanding applications. Advanced plastics offer excellent resistance to corrosion, chemical resistance, and environmental exposure, making them ideal for automotive, electronics, medical, industrial, and consumer goods applications. Not only can they replace metals in such cases, but they also reduce the weight of parts dramatically without compromising on structural performance. The reduced density of plastics, even when reinforced, aids the ergonomics, transport and distribution of finished goods.
Many polymers provide outstanding fatigue performance and long-term durability, even under repeated stress or harsh conditions. With the right material selection and design, plastics can deliver the mechanical strength, dimensional stability, and reliability required for critical components.
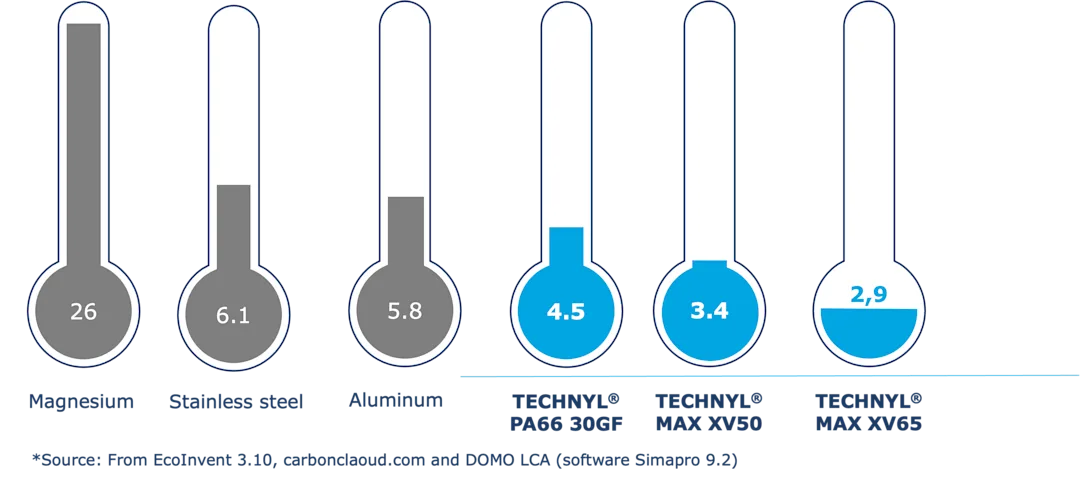
Environmental Benefits
Replacing metal with plastic can play a key role in achieving sustainability goals. Plastics typically have a lower carbon footprint than metals, both in production and throughout the product lifecycle. Many advanced polymers are recyclable, and bio-based or recycled-content options are increasingly available.
Manufacturing with plastics is often less energy-intensive than metals, further reducing environmental impact. By choosing sustainable materials and optimising designs for recycling, organisations can support circular economy initiatives whilst simultaneously meeting regulatory requirements.
New e-learning course!
Learn the best practices for replacing metal in your next project
The process of replacing metal with polymers isn't as straight forward as it may seem. It requires careful consideration from design to production.
To support you on this journey Ultrapolymers have collaborated with DOMO, producer of TECHNYL® polyamides, with an online course to support you in this process.






